In order to complete the project’s polished and professional appearance, in the 3D animation post-production stage, final touches are done. Post-production artists can change the look of a project without re-render the entire thing.
Any guesses how? Let us tell you.
You must have heard the term ‘Compositing in Animation’. In this brief guide, we’ll walk you through what compositing in animation is and how it works.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started.
An overview: What Is Compositing
First, 3D animation companies use compositing as the first stage in the post-production process. In order to produce a more coherent picture, the render passes from the production stage are combined or mixed with additional images or adjustment layers.
The technique might be as basic as matching two layers and altering their attributes, such as depth of field and color, or it can be as complicated as matching hundreds of layers.
Animation’s ultimate look comes to fruition at this point. If needed, specific 2D visual effects might be incorporated into the project.
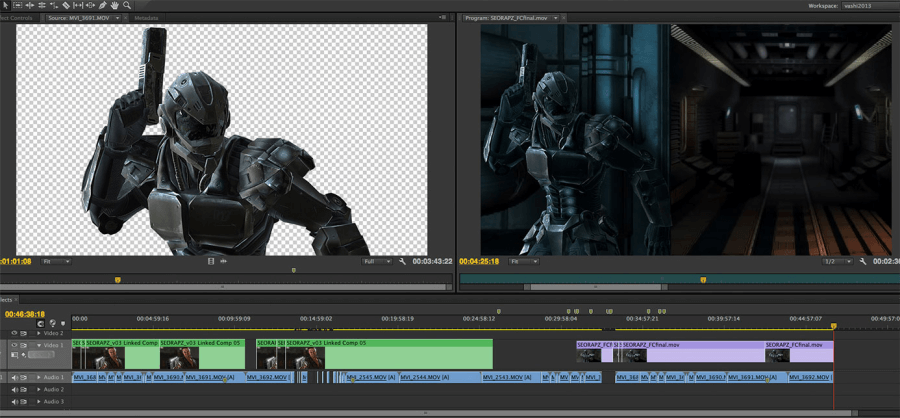
Compositing is an integral part of the 3D animation pipeline, and we’ll examine its role here. Let’s an example to demonstrate what compositing in 3D animation is done visually:
Compositing in 3D animation
Compositing is defined as creating a new image by fusing two or more existing ones. There are several ways to combine visual components from many sources to create a single scene’s appearance.
To generate a single image or set of images with predetermined features, compositing in 3D animation involves merging many render passes or adding layers. Compositing is one such method. Special effects, stage expansion, environment construction, blue/green screen replacement, and other techniques are all forms of compositing.
As long back as the 19th century, compositing methods were used. The vast majority of today’s compositing, including 3D animation, is carried out using digital software and tools.
Compositors at animation studios uses various compositing programs to modify and enhance digital renderings or add special effects.
Types of compositing in animation
Well, the most commonly known compositing types are the following:
- Particulate reinforced composites
- Fiber-reinforced composites
They are frequently used because they allow for a large variety of material combinations on various surfaces.
Usage of compositing in 3D animation production
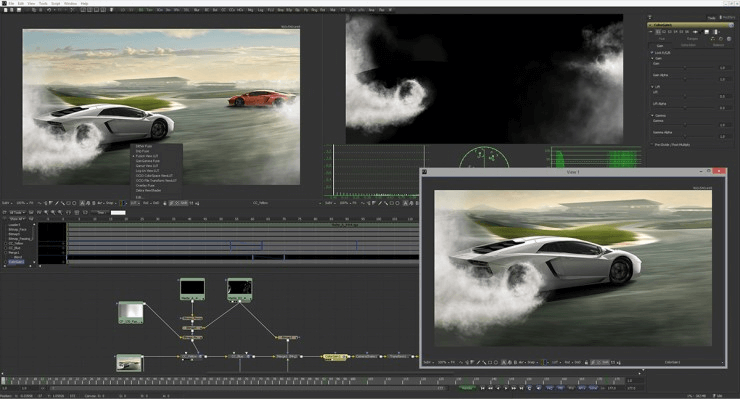
Source: nofilmschool
The compositing step in a 3D animation company can save time and money. Computers read enormous volumes of 3D data and perform countless computations in order to produce 2D pictures or frames during the rendering process.
Because of this, rendering can take a long time, even with the most powerful gear and software on the market.
It’s possible to fine-tune certain scene features by using render passes. Layers or Render Passes are commonly used to render a 3D scene. Allows for fine-tuning of the lighting, color, or other alterations and rendering of variations without re-rendering the entire picture. Additionally, each item can be displayed on its layer, obscuring the rest of them.
Let’s suppose these were rendered in 3D: Having to repeat the rendering process over and over again took up a lot of time and resources for the animation company. A single 3D object, for example, may need to be replaced rather than the entire scene being re-rendered if it has to be fixed.
As a result, most 3D animation companies have the final rendering stage following the compositing stage.
On the other hand, drawing a sequence of 2D photos after compositing is substantially faster than rendering a 3D project since no 3D data about every 3D component in the scene needs to be processed at this point.
It is necessary to mix, color-correct, and fine-tune the render passes and layers before sending them to the final rendering.
If you want to learn about 3D animation in detail, do give a read to how to make a 3D animation.
Compositing in animation: what is the process?
If the final scene needs to be re-rendered, all the teams involved in the project must re-engage in the rendering process to keep up with the changes.
Compositing does not necessitate re-rendering the whole footage because the 3D components are rendered independently.
In 3D production companies, the final rendering is done after only compositing because of this recurrence. This is how animation compositing works.
An insight into the professional life of 3d compositing artist
To create a screen-ready render, the compositing department at a 3D animation studio combines all of the 3D elements created by the previous departments in the 3D production pipeline (such as computer-rendered animation (CGI), visual effects (3D VFX), graphics (including 2D animation), live-action (CGI), and static backgrounds).

One of the most important responsibilities of a compositor is to ensure that all of the shots in a film meet the high standards set by the project’s stakeholders.
A large part of a compositor’s job at a 3D animation studio is integrating the 3D scenes while keeping an eye on the output’s technical and artistic elements.
Improving the colors, lighting, motion blur, and other 2D effects would be highly beneficial.
Composting also necessitates collaboration with other relevant disciplines. For this reason, an animation studio’s compositor must maintain effective communication within the team and strong interactions with other teams.
The key difference between 2D and 3D compositing
Because of technological advances, some may believe that 3D compositing is the superior choice. However, this is not always the case.
2D compositing is ideal for smaller-scale tasks since it is faster and easier to use. Try out a few options to find the setting that’s right for you.
Related Article:
In essence
Multiple render passes or layers are frequently used to create a 3D animated video’s many scenes. In the Compositing step, these layers will be reunited.
The initial phase in 3D animation post-production is taking the render passes from the production process, merging them, and then blending in extra modifications or pictures to make the composition more coherent.
Compositing is intertwined with 2D VFX, color correction, and final rendering, just as lighting, VFX, and rendering are.
A 3D animation studio’s compositing stage can save a lot of time and money. Compositors can make changes to a project’s aesthetic without having to re-render it, thanks to the tools and techniques they have at their disposal.
However, if you ever get stuck in your project and require some help. In that case, we highly recommend you to consult BuzzFlick – one of the best 3D animation companies that provide several 3D animation services at reasonable prices.
Related Articles:




